What is a Plastic Pump? Where is it used?
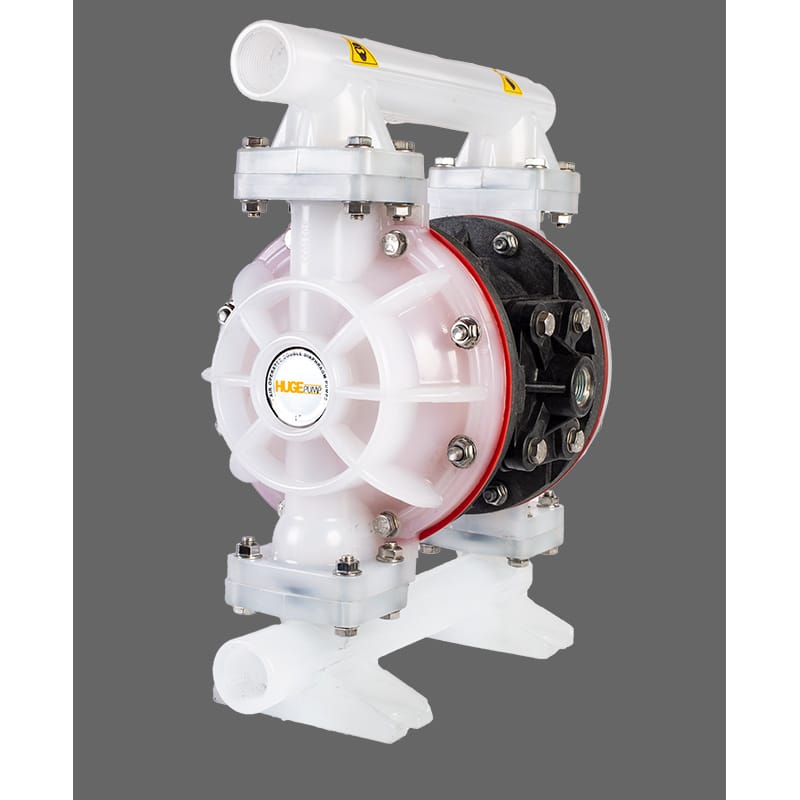
The plastic pump is designed for pumping chemicals such as acid, salt water, which can damage other types of pumps.
Plastic pumps are used to transport abrasive materials, acids, adhesives, chemicals, concrete and mortar, coolants, hazardous materials, liquid metals or lubricants. Since acidic chemicals are corrosive, they damage pumps such as metal and castings, rendering production dysfunctional.
Table of Contents
Plastic pumps are also used to move gasoline, diesel oil and oil; groundwater, drinking water, brine and waste water; sewage, sludge, slurry and ash slurry; gas and air; powders, solids and tailings; and can easily pump a variety of liquids and solids-containing fluids.

(Click here to readHow to Pump Acids and Chemicals)
What are the Characteristics of Plastic Pumps?
- These pumps have many features. Adjustable speed pumps can run at speeds selected by an operator, while continuous duty pumps are also available.
- Pumps with dry running capability can operate for long periods without pumped liquid or external lubrication.
- Self-priming pumps are designed to create and maintain a vacuum level sufficient to draw liquid into the inlet without outside assistance.
- Some auxiliary pumps include battery backup, pressure gauge, level controller, thermal overload protection or suction.
- Other pumps are close coupled, corrosion resistant, multistage, reversible, portable, plug-in or sealed.
- Sanitary, hygienic and washdown duty models are also available.
- Non-clog pumps can move sticky or stringy materials.
- Pumps with strainers or filters collect solids.
- Important specifications for brine pumps include maximum discharge flow rate, maximum discharge pressure, inlet size, discharge size and media temperature.
- Power sources include alternating current (AC), direct current (DC), compressed air, gasoline, diesel fuel, hydraulic systems, natural gas, water and solar energy.
Where are Plastic Acid Pumps Used?
- It is used in commercial, industrial, municipal and marine applications.
- Examples include agriculture and horticulture, dairy farms, breweries and distilleries, construction, flood control, food service and food processing, electricity generation and oil and gas production.
- Plastic pumps are also used in the aerospace and defense, automotive, machinery, mining, medical, pharmaceutical, semiconductor and paper industries.
- Devices for heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are also available.

What are the Advantages of Plastic Pumps?
These pumps normally require less maintenance and are resistant to acidic media and corrosion.
They are also generally lighter than metal pumps of the same type.
Teflon is often the preferred specialty plastic polymer due to its stronger and more durable construction. This is especially true in heavier industrial environments, but other types of plastic can also be used, such as PVDF, Polypropylene, Neoprene, Santoprene, Viton and Buna-N.
In harsher environments, plastic pumps are cheaper than metals as special high grade cast metals do not need to be used where plastics are to be made.
What are the Disadvantages of Plastic Pumps?
- Limited pressure ratings
- Reduced impact resistance
- Narrower temperature ranges, (They are normally more susceptible to heat damage and therefore may have a lower maximum temperature limit.)