What is a Gear Pump? What are the Features?
The gear pump has rotating gears and allows liquid transportation by rotating. It pushes the liquid with the vacuum pressure it creates. Let’s continue for more.
Table of Contents
It has the ability to create very high pressure. Invented by Johanner Kepler in the 1600s. Widely used in chemical plants for pumping high viscosity liquids.
Unlike the centrifugal pump, which converts speed into pressure, the displacement pump moves the liquid using mechanical movement. Reciprocating and rotary types are available.
Working Principle
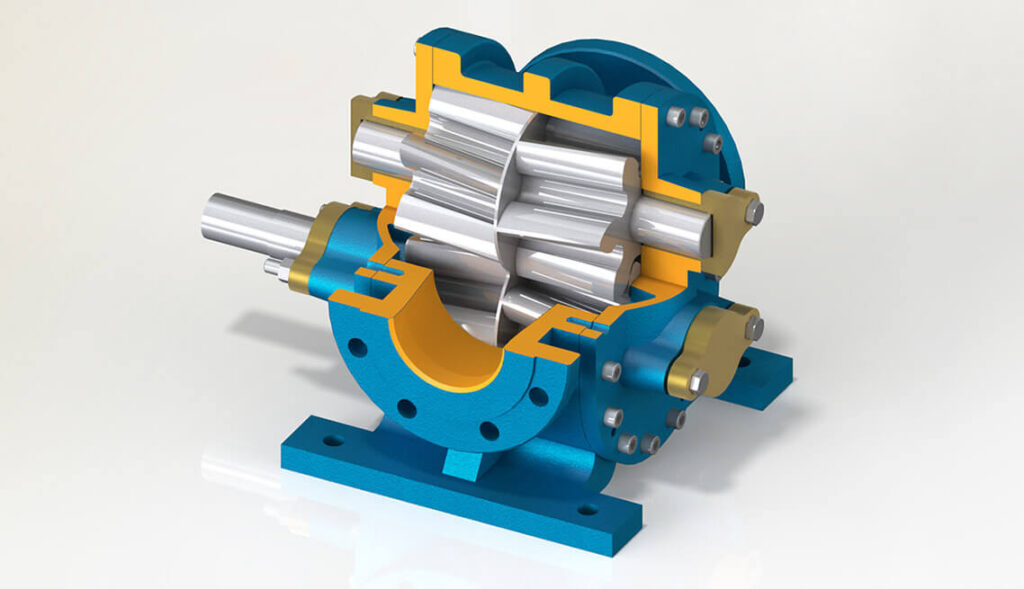
Gear pumps are positive displacement, i.e. they push a constant amount of fluid per revolution. The rotating assembly of the idle and drive gear creates suction at the pump inlet and the fluid moves by pulling.
The volume of the liquid directed to the discharge point between the gears decreases with the movement and allows the pressure to increase.
The flow in gear pumps is determined by the rotational speed (rpm) and the amount of slippage, which determines the volume and the amount of rotation between the pump teeth.
The rotation speed and tight mechanical clearances minimize the amount of liquid flowing in the wrong direction. This way the pump works more efficiently.
Features
Gear pumps are compact and simple pumps with a limited number of moving parts. Although they do not match the pressure produced by piston pumps or the flow rate of centrifugal pumps, they offer greater efficiency than valve pumps. They are particularly suitable for pumping oils and other high viscosity liquids.
It is mainly used for measuring and mixing operations and can be used to handle aggressive liquids. They are usually made of cast iron or stainless steel.
Areas of Use
Used for pumping high viscosity liquids such as oil, paint, resin or foodstuffs. In applications where accurate dosing or high pressure output is required, it is preferred in irregularly fed systems where the pump output is not affected by pressure.
- Automotive fuels and lubricants
- Hydraulic oils
- Alcohol and solvents
- Circulation of hot oil
- Paint, resins and polymers
- Liquid soap
- Edible foods such as corn syrup, animal feed and peanut butter

Varieties
It is generally divided into 2 as external or internal gear pump.
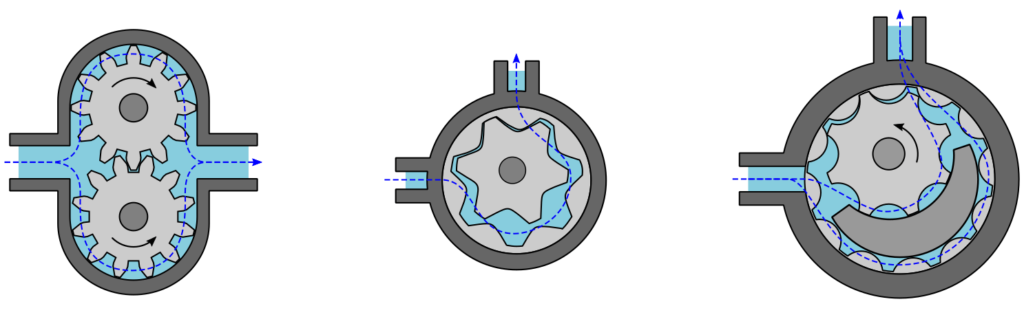
External Gear
Hydraulic power application is used in lifting machine, mobile plant equipment. It is used to provide power in areas where electrical equipment is bulky, costly or inconvenient. Medium efficiency and low cost compared to other types. It is used to transfer fuel oils such as gasoline, diesel and kerosene.
Internal Gear
Also known as an internal gear pump, it has intermeshing gears with internally cut teeth and produces flow. Once the gears exit the mesh, liquid is drawn into the pump.
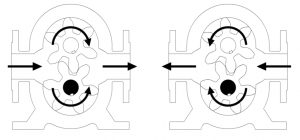
The liquid flows into the cavities and discharges from the inlet around the casing. As the teeth of the gears engage on the discharge side of the pump, the volume is reduced and the liquid is discharged under pressure.
Helical Gear Pump
Positive displacement pump type that transmits the movement to the gear together with the shaft consisting of 2 parts. While the rotating gear transmits its motion to the rotating gear, it is separated and a vacuum is created. Thanks to the vacuum, the liquid is drawn in and moves through the tooth cavities towards the discharge port.
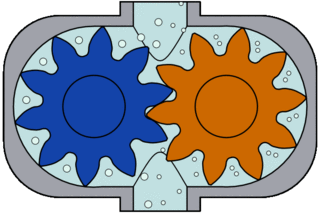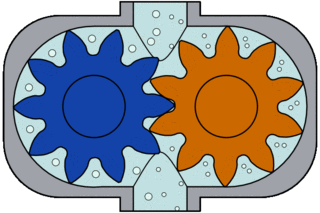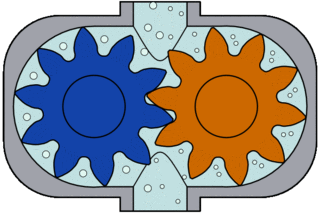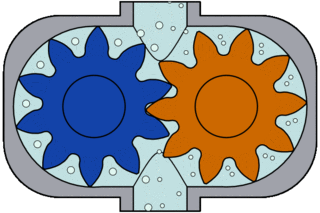
From the discharge nozzle, the gears mesh with each other, creating pressure and the liquid is discharged. The amount of liquid transported is directly proportional to the size and speed of the pump.
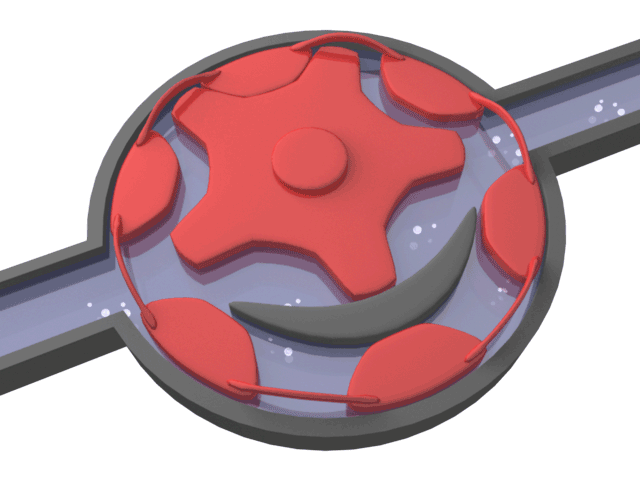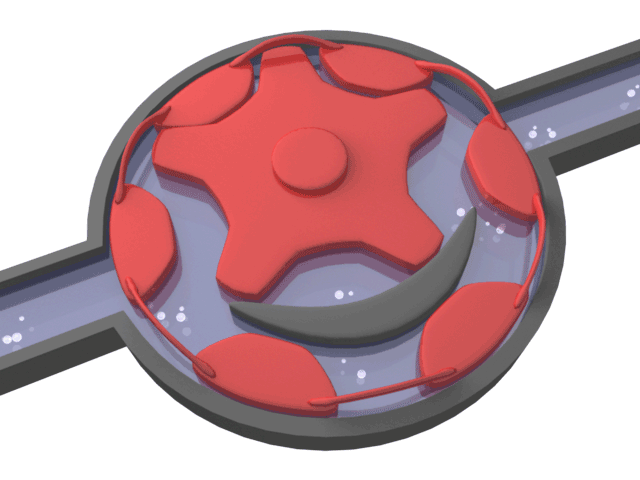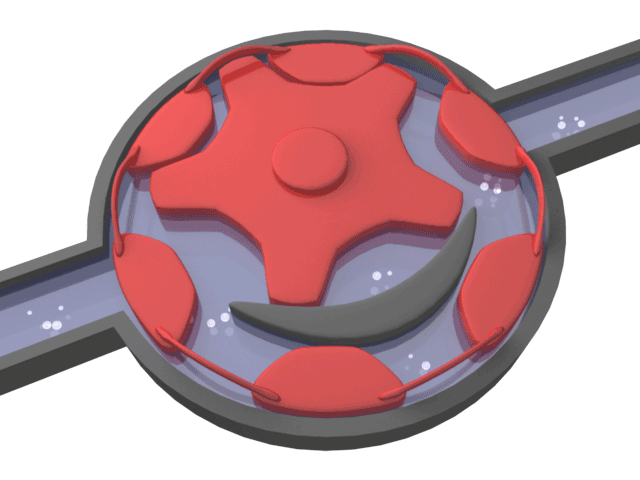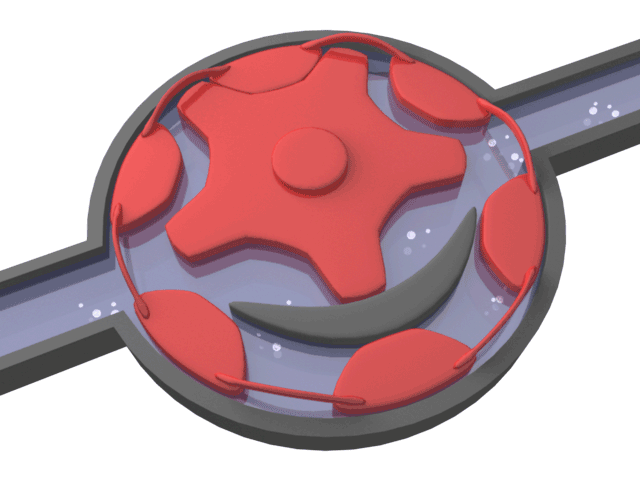
Helical gear pumps operate with high efficiency where silent operation and uninterrupted flow rate are desired. It has the ability to pass small and crushable particles in the liquid.
Spur gear pumps work efficiently in the transfer of abrasive liquids, non-lubricating liquids and high temperature liquids where medium pressure is required.
Gear Oil Pump Advantages and Disadvantages
They are preferred due to their compact size and simple design. They are more reliable than complex pumps because they have few moving parts. The transported liquid is self-lubricating. It cannot run dry for a long time.
It is sensitive to abrasion and when abrasion occurs, leakage occurs and pump efficiency decreases. If it is to be used with abrasive solids, pressure should be low, flow should be high and operating speed should be low. A pressure relief device must be installed.
Although it is not recommended for use with corrosive substances and liquids containing solids, internal gear types are more suitable than external gear types. This is because the loose mechanical tolerance range allows this. Internal gear types can cope with lower viscosity, especially for low viscosity fluids, as the leakage rate is high.
Gear Pump Prices and Detailed Information
Click here for detailed information about water pumps. Click here for gear pump prices.


