What is a Heat Exchanger? Plate Heat Exchanger
A heat exchanger is a device made to transfer heat from one fluid to another. Its suitability for a fluid depends on the type of plate exchanger, heat exchanger type material used.
Table of Contents
In principle, plate type exchangers are divided into three types;
– Tubular,
– Plate type, (Detachable type, Welded type, Semi-welded type, Brazed type)
– Special application (Platecoil, Econocoi, Spiral)
Heat transfer between the fluids of cooling systems and heating systems is provided by plate and heat exchangers depending on the flow rate it has without mixing with each other. The heat of the fluids is transferred in the pre-exchanger of the plate located in the plate with the higher heat between the two plates.

Areas of Use of Heat Plate Exchangers?
It is generally used to cool or heat buildings and to make engines or machines run more efficiently.
1. Natural Gas Combi Boilers
2. Air Conditioners
3. Refrigerators
4. Automobile radiators
5. Air Curtains / Economizers in Thermal Power Plants
6. Regenerators in Gas Turbines
7. Petro-Chemical Industry / Refineries
8. Beer and Wine Making Industries
are the main areas of use.

In buses, for example, the liquid used to cool the diesel engine is usually passed through a plate exchanger. The recovered heat is used to heat the cold air from outside, which is pumped through the floor of the passenger compartment.
This eliminates the need to have additional electric heaters inside the bus.
In homes, it equalizes the temperature of hot water coming from places such as combi boilers, heating boilers and boilers without mixing it with cold water coming from the network. There is no energy cost for this process.
In simpler terms, a 30-plate plate heat exchanger has 2 inlet and 2 outlet chambers.

Hot water enters at the inlet, circulates through 15 plates and exits through the outlet at the bottom. Likewise, cold water enters at the inlet, circulates through 15 plates and exits at the bottom.
Since there will be heat transfer between the plates, the hot water entering from the inlet cools while the cold water heats up. Both water coming out of the outlet will be equal to each other.
Heater Exchanger Types
It consists of a large number of small tubes contained in a cylindrical rod. The tubes are inserted into the cylinder with fixed tube plates (permanently fixed to the body) using a tube bundle or “tube stack”.
They have a structure that accommodates changing temperature conditions and at the same time allows the pipe bundle to be easily removed for service and maintenance.
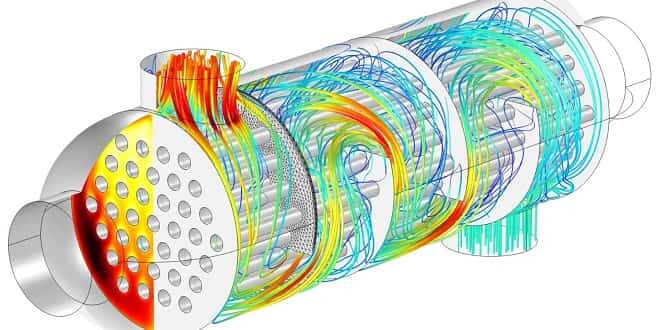
- The front end is where the fluid enters.
- The back end is where the fluid exits or returns to the front header in heat exchangers with more than one tube passage.
- The tube bundle includes tubes, tube layers, baffle plates and connecting rods.
Thetubular type heat exchanger is often used for heat recovery in processes that consume hot gases. The heat from the gas is transferred to a liquid, usually water or a thermal oil. The heated liquid can then be used in an application where you would normally use more energy.
Ideal for chemical applications, petrochemical cooling, steam cooling, textile processing, grain drying, concrete curing, paper production and food processing.
Plate Heat Exchanger
Plate exchangers separate heat exchanging fluids by means of plates. These normally have reinforced surfaces such as fins or embossing.
They are bolted, brazed or welded together. It is commonly used in heating and cooling systems to transfer heat in heat transfer surface heat plate exchangers.
It consists of fins or spacers sandwiched between parallel plates. The fins are arranged to allow a combination of cross flow or parallel flow between adjacent plates.
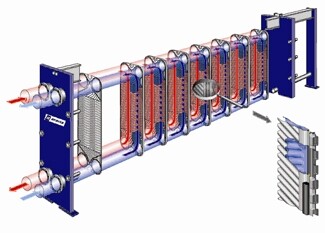
- Hot water Inlet and Outlet
- Cold water inlet and outlet
- License plate compartment
Plate heat exchangers are generally used in combi boilers, heating boilers, boilers, air conditioners.
Flow Types of Heat Exchangers
There are four basic flow options:
- Counter flow
- Simultaneous Flow
- Cross flow
- Hybrids such asCross Flow and Multi-pass Flow
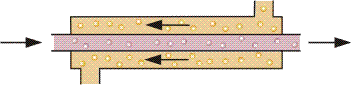
It shows an idealized reverse flow exchanger in which two fluids flow parallel to each other but in opposite directions. This type of flow arrangement allows the largest variation in temperature of both fluids and is therefore the most efficient

In simultaneous flow heat exchangers, the flows are parallel to each other and flow in the same direction as shown in Figure 2. This is less effective than countercurrent.
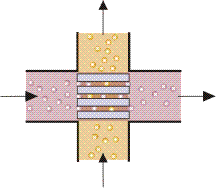
Cross-flow heat exchangers are intermediate in efficiency between counter-current and parallel flow exchangers. In these units, the flows are at right angles to each other as shown in Figure 3.
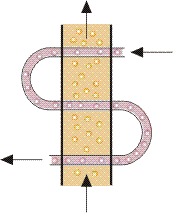
In industrial heat exchangers, hybrids of the above flow types are often found. Examples of these are combined cross-flow/reverse-flow heat exchangers and multi-pass flow heat heat exchangers.
You can contact us about a Heat Exchanger you have bought / will buy, or you can get information by contacting our Technician friends from 444 5 622 Call Center.
Do you have any other questions about Heat Exchangers?
Click here for current plate heat exchanger prices.
Is there anything left unmentioned?
You can specify by commenting…
Visit our hardware installation category.

