What is an Air Diaphragm Pump?
Air diaphragm pump used for various purposes in many fields of industry. It is operated by connecting an air pump to a compressor with a capacity suitable for the pump size.
Table of Contents
It has a non-explosion feature because it does not work with electricity and does not contain any electrically operated parts. Diaphragm pumps working with different pressure values are similar to suction and discharge pumps.
Air operated, double diaphragm type pumps are made safer for ex proof areas thanks to the air valve. These air operated positive displacement pumps are preferred for liquid transfer in flammable environments.

What are the Usage Areas of Diaphragm Pumps?
Diaphragm pumps are used in many applications, especially in industrial applications.
- Muddy wastes,
- Corrosive chemical
- Volatile solvents
- Viscous, sticky liquids
- Slip-sensitive foodstuffs and pharmaceuticals
- Dirty water and abrasive slurry
- Small solids
- Creams, gels and oils
Air Diaphragm Pump Types and Heat Dissipation
| Neoprene | Maximum Minimum |
| Very good resistance to vegetable oils. Acids, esters, ketones are not preferred transfer fluids because they damage the material structure. | 90 ˚C -22˚C |
| Buna-N | |
| Generally used in oils. High resistance to use in water, hydraulic oil transfers. | 87 ˚C -22˚C |
| EPDM | |
| Good resistance against chemicals. It cannot show much resistance against oil and solvents. Resistance to alcohols and ketones is moderate. | 138 ˚C -40˚C |
| Teflon | |
| Generally used in heavy chemicals and acids. Very good resistance. Very suitable for fluid transfer at high temperatures. | 100 ˚C -35˚C |
| Viton | |
| Very good resistance to acids, oils and solvents. | 175 ˚C -40˚C |
| Santoprene | |
| Good resistance to medium and weak acids. high abrasion resistance. | 135 ˚C -40˚C |
| Polipropilen | |
| Good resistance to acids. Preferred in food, chemical and cosmetic products | 82 ˚C 0˚C |
How Does a Diaphragm Pump Work?
Air diaphragm pumpsuse compressed air as power source. They also include a diaphragm in each chamber and two chambers with inlet check valve and outlet check valve.
The air supply is shifted from one chamber to another by an air spool valve built into the pump.
The continuous displacement of air from one chamber to another (to the back side of the diaphragm) pushes liquid from one chamber and into the discharge pipe while the other chamber is filled with liquid.
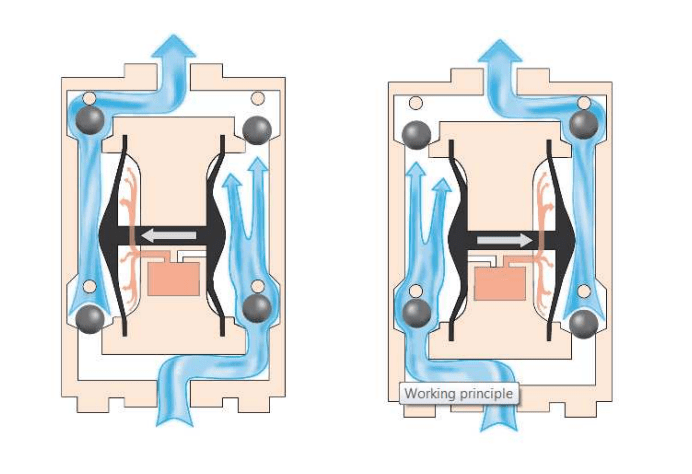
To put it more simply, think of the injection syringes we often encounter in hospitals. The way syringes work is actually based on the way diaphragm pumps work.
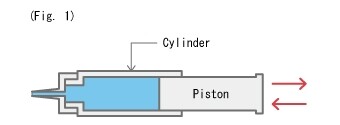
When the piston retracts, as shown in Figure 1, the liquid is drawn into the cylinder. When the plunger is pushed forward, the liquid is discharged through the injection needle at the end of the cylinder.
Let’s look at a model where the fluid enters and exits at the same point as an injection syringe, but with separate inlet and outlet points.
(In this example, the inlet and outlet flow paths are both circular.)
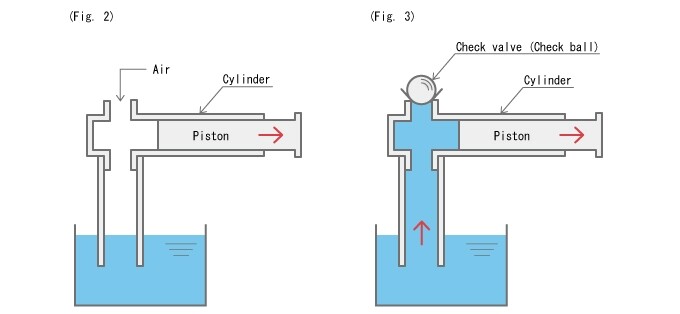
Does the cylinder suck the liquid when the piston is pulled out in Figure 2?
The answer is no. Even if the piston is moved outwards, it only sucks in air from the top of the cylinder from the withdrawal of the liquid.
Now, in Figure 3 we will place a spherical check valve above the air entering. Then, as shown in Figure 3, the air no longer flows and a pressure builds up that sucks the liquid into the cylinder. .
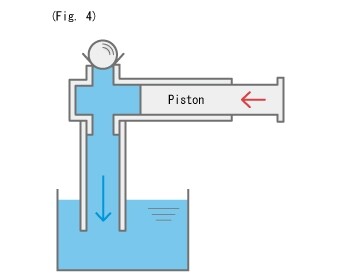
(Fig. 4)
If the check valve is very light, some liquid may be discharged, but mostly it returns to the tank.
If the check valve is quite heavy, all the sucked water will return to the tank.
Now place another check valve at the bottom of the cylinder in the direction to stop the backflow.

In this case, due to the lower check valve, the liquid in the cylinder does not return to the tank, as shown in Figure 5, and pushes the upper check valve up and flows out.
When the piston moves outwards, this time when the upper check valve closes, the lower side opens and the liquid is sucked into the cylinder.
Note that there is no backflow from the upper side at this time. (Figure 6)
As shown here, a check valve works so that the fluid moves in one direction, a key function required for a diaphragm pump (piston pump).
In general, a check ball is used as a check valve.
Diaphragm Pump Design
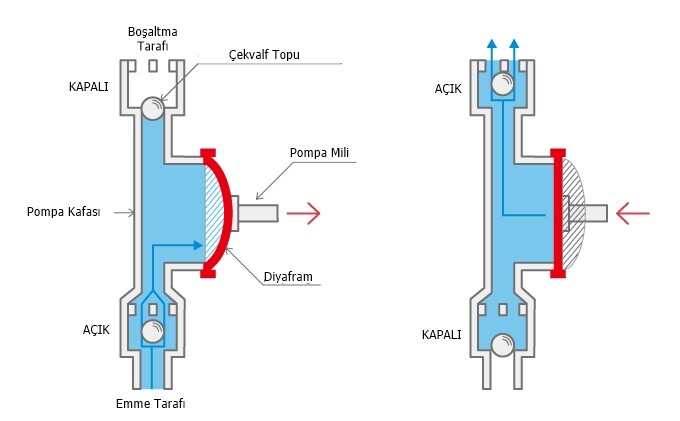
Features of Diaphragm Pumps
Based on the above operating principle, diaphragm pumps have the following characteristics.
- Pulsating Liquid Flow: Due to the principle of operation, the liquid flows intermittently due to the suction and discharge process. This is called pulsation, which makes diaphragm pumps fundamentally different from centrifugal pumps (explained in detail later).
- When fluid enters the cylinder through a check valve operation, it always flows out the top side: Therefore, even if a significant pressure is applied to the discharge side (top side), by keeping the ball check valve depressed, the pressure inside the cylinder increases as long as the force (force pressing on the piston) allows it.
- Theoretically speaking, in closed operation, this means that the pressure inside the cylinder can increase infinitely. However, before the pressure reaches infinity, the weakest parts near the pump, such as the cylinder or discharge side piping, could burst or the engine driving the piston could burn out.
- This is the reason why the relief valve and the thermal relay of the motor must never be released when using a diaphragm pump.
- Check Valve Sealing : When debris or foreign matter enters around the check valve, the sealing is compromised. In such a case, the return function is disabled and this severely impairs pump performance, in some cases stopping the pump from discharging completely.
- The same situation can occur when the check valve or valve seat (the part that contacts the check valve to form a seal) is damaged. If the check valve and valve seat are dry, air passing through the slight gaps between the irregular surfaces can affect the sealing performance.
- (If the pump is above the tank: suction situation). In such a case, wetting the check valve and the valve seat with liquid increases the tightness and makes suction and discharge possible.
Diaphragm Pump Selection
Diaphragm Pump Prices

Since diaphragm pump prices are generally imported products, they may vary according to the Dollar and Euro exchange rate. Kampa works with local brands to support domestic capital and keep costs to a minimum.
Diaphragm Pump Repair

As with any mechanical device, diaphragm pumps may fail from time to time.
We frequently encounter reasons such as dirt getting stuck in the check valve, rupture of the diaphragm, and breakage in cases such as falling and hitting.
But as everything has a master, the repair of these pumps should be done in their own technical services.
It is possible to have a diaphragm pump repaired through technical services that do not have spare parts shortage and have a solid technician staff.
You can contact Kampa Technical Service team for repair and maintenance of your pumps.
We have explained Diaphragm Pumps above. Is there anything left incomplete or stuck in your mind? If you let us know in the comments section, we will be happy to answer here. Click here for detailed information about the pumps.
Details of other products will be added soon. Don’t forget to subscribe to be informed about new content.