Design and Operation of Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal pumps are the most widely used pumps in agricultural and industrial processes. They are used in water pumping, pressure boosting, waste water, water supply, heating and cooling distribution and other industrial applications.
What is a centrifugal pump? In simple terms, a centrifugal pump is a machine that allows the transfer of a liquid to a higher place. These pumps belong to the class of rotary machines.
Centrifugal pumps were first designed in the late 1600s. Since then, they have been renewed and remained popular until today.
Working Principle of Centrifugal Pumps
Normally a centrifugal pump consists of an impeller filled with liquid. This liquid can be anything, but in most cases it is water. . A component inside the impeller rotates rapidly, causing the liquid to be subjected to centrifugal force. Due to this force, the liquid travels to the discharge opening.
When the water is evacuated, a vacuum is created, leading to the formation of atmospheric pressure that forces more liquid through the casing. One reason why this movement is seamless is that the blades on the impeller are curved.
The rotation of the impeller gives the liquid at the tip a centrifugal force that is proportional to the velocity at the wing tip. When the liquid exits, it has kinetic energy. This kinetic energy is also converted into pressure energy due to the resistances in the discharge nozzle and the pump volt.
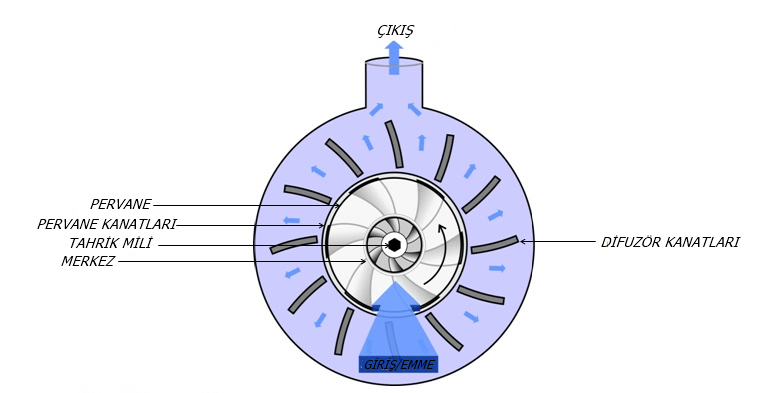
Centrifugal Pump Design
The mechanical and hydraulic suitability of a centrifugal pump is crucial to the efficiency and reliability of the system. Oversizing a pump can cause recurring problems throughout the lifetime of the system.
The factors are for both mechanical and hydraulic characteristics of the pump. Mechanical considerations are pumping conditions, pump sealing and impeller geometry. Hydraulic considerations include suction point, flow rate, fluid characteristics and system resistance.
When designing or installing a centrifugal pump you cannot ignore the suction conditions. An important concept in this area is the Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH), this is the head required at the suction of the pump for specific operating conditions.
The required NPSH depends only on the manufacturer design of the pump: casing, impeller, nozzle… these data are given as a curve by the manufacturer and the available NPSH depends on the suction condition of the pump: fluid pressure, temperature, fluid pressure vapor, suction head or suction lift… these data are calculated by the designer of the pump.
A centrifugal pump has two main parts – the stationary part and the rotary part. The parts are shown in the figure below. The stationary parts are the casing, the nozzle and the bearing housing.
Rotating parts include the impeller and shaft. Apart from these main parts, the centrifugal pump also comes with auxiliary components that include cooling, control and lubrication systems for others.
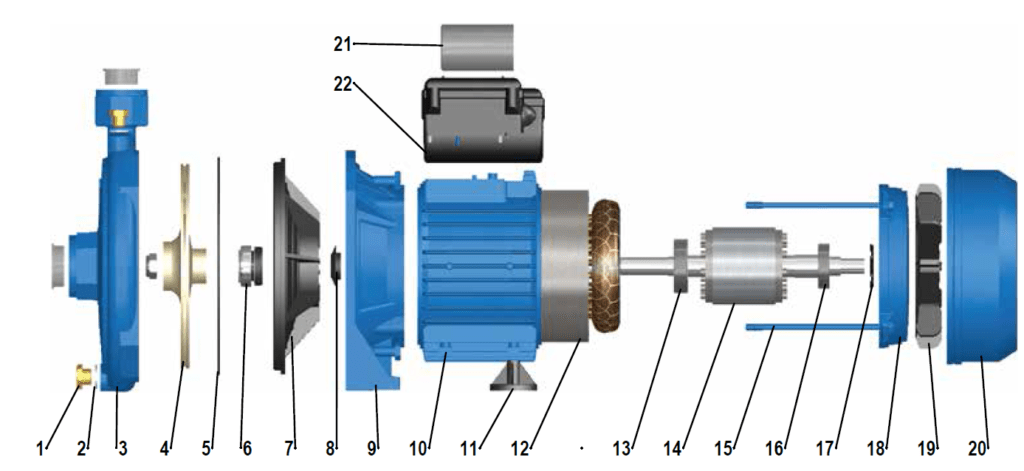
- Buy tapa
- Blind plug gasket
- Transceiver housing
- Wheel
- Transceiver body oring
- Mechanical salmasta
- Disk
- Water deflektor
- Foot
- Engine Housing
- Engine support leg
- Coiled stator
- ön Rukman
- Mile Pebbled Rotor
- Engine Stud
- Rear bearing
- Bearing thrust spring
- Rear bearing cover
- Cooling Fan
- Fan Housing
- Capacitor
- Klemens Kutusu
There are many design options when choosing pump parts : monoblock or split case, double suction, end suction, in-line, closed or open impeller, horizontal or vertical construction, single stage or multistage…. The manufacturer has different products with different combinations of parts to achieve specific process requirements.
Hydraulic Selection of Centrifugal Pumps
When it comes to selecting a centrifugal pump: capacity, suction and discharge head are critical parameters. They are characterized by the following general steps in the selection of a centrifugal pump.
Determining the Actual Flow Rate
Flow rate refers to the volume of liquid transferred per unit time by a pump. This parameter is determined by the process and the number of pumps to be installed. You can see it as m3/h or l/min in some pump curves.
Determining the Static Head
Static head refers to the difference between the elevation of the highest point to which you want to deliver water and the elevation of the water source.

Determining the Friction Head
To calculate the head loss due to friction, you need to consider all the elements present in the piping system connected to the pump: pipe, fittings, valves… calculations are made based on the resistance characteristics of these elements and the frictional properties of the fluid.
Selection of Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal pump manufacturers produce pumps for specific purposes. Pump curves are shaped in height and flow rate to help you choose a pump. Read our other article on how to read pump curves.
Select the most efficient option among the possible pumps and check that the NPSH required by the pump is lower than the NPSH available in the installation to ensure that the liquid will not cause malfunction or cavitation of the pump.
Other considerations such as the size of the impeller or the position of the duty point on the curve must be taken into account. Click here to review and purchase centrifugal pump prices.
Daha detaylı santrifüj pompa seçimi için diğer makalemizi okuyabilirsiniz.

