Inverters and Energy Conversion: A Comprehensive Guide 2025
Today, electrical energy has become an indispensable part of our lives. Inverter is used in areas where electrical energy needs to be used in different forms and frequencies.
Inverters are devices that convert electrical energy from direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). In this article, we will examine in detail what inverters are, how they work, their usage areas and different types.
One of its advantages is that it saves energy. Therefore, its use plays an important role in reducing energy costs.
Inverter technology is one of the most critical components of energy conversion. Today, it is used in many areas and this increases its importance.
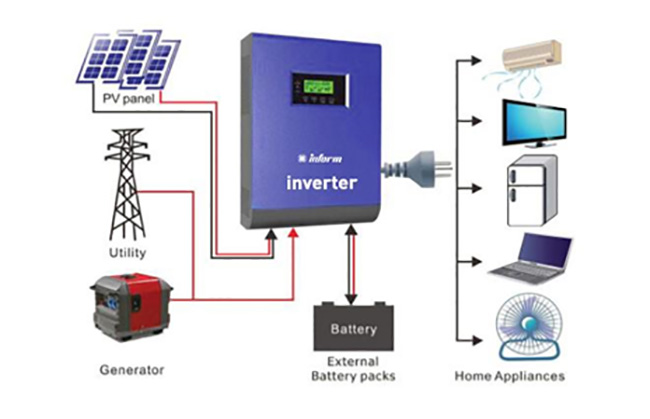
What is an Inverter?
Power converters, especially those used in solar energy systems, are widely preferred devices in household and industrial applications. These devices ensure the efficient use of electrical energy.
An inverter is a power electronic device that converts DC electric current into AC electricity. This conversion is necessary for the operation of electrical appliances and to ensure grid compatibility. In solar energy systems, DC electricity stored in batteries can be converted to AC by inverters. This is used in households and industry.
Not only can they convert DC to AC, but they can also regulate electrical parameters such as frequency, voltage and waveform. This allows them to be used in sensitive processes such as motor speed control.

History and Development
The foundations of invert technology date back to the first power conversion studies in the field of electrical engineering. While early examples were based on mechanical systems, today they have become much more efficient and compact thanks to advanced semiconductor technologies. Especially with the spread of renewable energy systems, power converter technology has gained great momentum.
How Does Inverter Work?
The working principle is quite simple. First, the DC voltage is cut. Then it is converted into AC waveform with a suitable filtering. This is usually done using high frequency electronic switches. The switches are switched on and off at certain frequencies so that the output waveform is smooth.
The basic working process is as follows:
- Direct current source: DC power is applied to its input (battery, solar panel, etc.).
- Switching circuit: Transistors or MOSFETs are used, which quickly interrupt the DC current.
- Conversion circuit: The pulsed output from the DC is processed by a transformer and filter. This process converts the output into a pure sine wave or a modified sine wave.
- Output power In the final stage, the converted AC voltage is transmitted to appliances or to the grid.
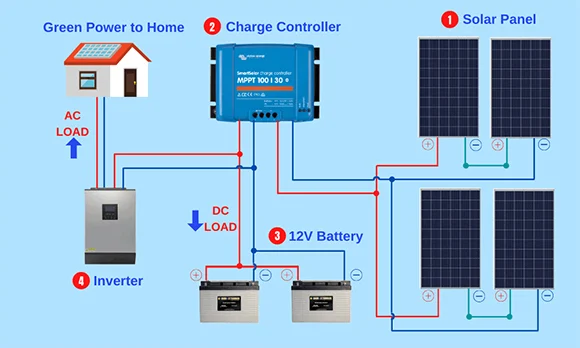
Inverter Types
They are divided into different categories according to their area of use and the AC waveforms they produce:
According to Waveform
a) Modified Sine Wave
It generates simple waveforms and is generally inexpensive and low cost. However, it is not fully compatible with sensitive electronic devices. It is suitable for household appliances, small motors and simple electrical devices.
b) Pure Sine Wave
It is more complex and produces an AC waveform that is closest to the mains electricity. Ideal for precision instruments, medical equipment, high-efficiency motors and solar energy systems.
According to Area of Use
a) On-Grid
These devices are used in grid-connected systems and convert DC electricity from solar panels into AC and transmit it to the grid. They are widely preferred in solar power plants and home solar energy systems.
b) Off-Grid
Suitable for off-grid systems. Especially for chalets, campsites, boats and rural areas. It usually works with battery support.
The development of power exchanger technology contributes to the proliferation of sustainable energy solutions. Therefore, its role in the future will become increasingly important.
c) hybrid
Both grid-connected and stand-alone types work integrated with battery storage systems. Today, they have become very popular in terms of energy management.
Areas of Use
It plays a critical role in many sectors:
- Solar Energy Systems: Solar panels convert the DC electricity they generate into AC. This is suitable for exporting electricity to the grid or for home use.
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): During a power outage, it converts the energy stored in the battery to AC to keep the devices running.
- Electric Vehicles (EV): Electric vehicle motors run by converting DC energy stored in the battery into AC.
- Home Appliances and Electronic Devices: Laptop adapters, portable power supplies and motorized devices use inverter technology.
- Industry and Industry: Used for motor speed control, energy saving and process management.
Technical Specifications and Performance Criteria
- Efficiency: ranges from 85% to 98%.
- Power factor An important criterion that determines the efficiency of the output power.
- Waveform and frequency sensitivity: Critical for grid compatibility.
Integration with Energy Storage Systems
It is used to provide uninterrupted energy by working integrated with battery systems. Inverters that can work together with lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries offer great advantages, especially in solar energy systems.
Its various types offer solutions suitable for different applications. This diversity allows users to choose the most suitable inverter according to their needs.
Smart Inverters and IoT Integration
With advancing technology, Wi-Fi enabled inverters enable remote monitoring and control. This improves energy management. Thanks to smart algorithms, it analyzes energy consumption and ensures efficient operation.
Comparison of Inverters: Models and Brands
Models from different manufacturers can be compared in terms of power capacities, efficiency ratios and additional features. Among the most popular brands are SMA, Huawei, Fronius, Victron Energy and Schneider Electric.
Things to Consider When Choosing an Inverter
You should consider the following criteria:
- Power Capacity: It must meet the total power of the devices to be connected.
- Power Capacity: It must meet the total power of the devices to be connected.
- Productivity: High efficiency types that can operate with low losses save energy.
- Protection Features: Models with overload, short circuit and over temperature protection are safer.
Legislation on the use of inverters is designed to ensure the safety of users. Therefore, it is important to consider the current regulations when using them.
Advantages of Use
- Flexibility: Facilitates the use of alternative energy sources.
- Energy Efficiency: Saves energy in applications such as motor speed control.
- Uninterruptible Power Can be used as a power source during power outages.
- Environmentally Friendly: Integrates with solar and wind energy systems to provide clean energy.
In the future, inverter technologies will become smarter and more efficient by combining with innovative solutions such as artificial intelligence. This will offer great advantages for users.

Failure Conditions and Maintenance Recommendations

- Common Failures: Overheating, under-voltage problems, output waveform errors.
- Maintenance Recommendations: Remove dust and dirt, check connection points regularly.
Legislation and Standards for Use
Worldwide, inverters are required to have certificates such as CE, ISO, IEC. In Turkey, regulations set by EMRA and TEDAŞ contain important rules for grid connection.
Future Directions of Inverter Technology
Future Directions of Inverter Technology
Sonuç
They are an integral part of energy management in the modern world. From households to industry, from portable appliances to large-scale power plants. Click here for detailed information on solar pumps.
By choosing the right inverter, you can both increase energy efficiency and operate your appliances more safely. Especially when combined with renewable energy systems, inverters are an important investment for a sustainable future. Click here for solar inverter prices.


